CBSE Class 10 Geography Chapter 6 Notes serve as a valuable resource for students preparing for the Social Science subject. Since the subject is mostly theoretical, making notes while studying helps in better understanding and retaining the key concepts. Well-organised notes not only simplify learning but also make revision more efficient. To aid students in their preparation, we provide well-structured and easy-to-understand CBSE Class 10 Geography Notes. These are prepared by experienced subject experts. These notes are designed to enhance learning effectiveness and prepare students for exams.
Class 10 Geography Chapter 6 Notes
Introduction
- Manufacturing refers to the large-scale production of goods by processing raw materials into more valuable and useful products.
- Manufacturing industries are part of the secondary sector of the economy.
- The growth of manufacturing industries is an important indicator of the economic strength and progress of a nation.
Importance of Manufacturing
The manufacturing sector is considered the backbone of overall development, especially economic growth, for the following reasons:
- Manufacturing industries play a crucial role in modernising agriculture, which is the foundation of our economy.
- It creates employment opportunities in the secondary and tertiary sectors.
- It contributes significantly to reducing unemployment and poverty by creating a large number of jobs.
- Exporting manufactured goods helps earn valuable foreign exchange, thereby boosting the country’s economy.
- It transforms raw materials into a diverse range of high-value finished goods, thereby contributing to industrial growth and consumer satisfaction.
Industrial Location
Industrial locations are often complex and depend on several key factors such as the availability of raw materials, labour, capital, power and access to markets. It is rare for all these resources to be found in one place, so industries are usually set up in places where these factors are either naturally available or can be arranged at low cost.
Cities play a vital role in supporting industries by providing markets and essential services such as banking, insurance, transport, skilled labour, consultancy and financial advice.
Agriculture and Industry
Agriculture and industry are interdependent.
→ Industries give a big boost to agriculture by increasing its productivity by providing their equipment and products like fertilisers, etc.
→ Industries depend on agriculture for raw materials and sell their products like irrigation pumps, fertilisers, pesticides, plastic and PVC pipes, machines and equipment, etc., to farmers.
Contribution of Industry to the National Economy
The contribution of industry to GDP in India is very low compared to East Asian economies.
- The National Manufacturing Competitiveness Council (NMCC) has been set up by the government to take appropriate policy measures to improve the productivity of the manufacturing sector.
Classification of Industry
Based on the source of raw materials used:
→ Agro-based
→ Mineral-based
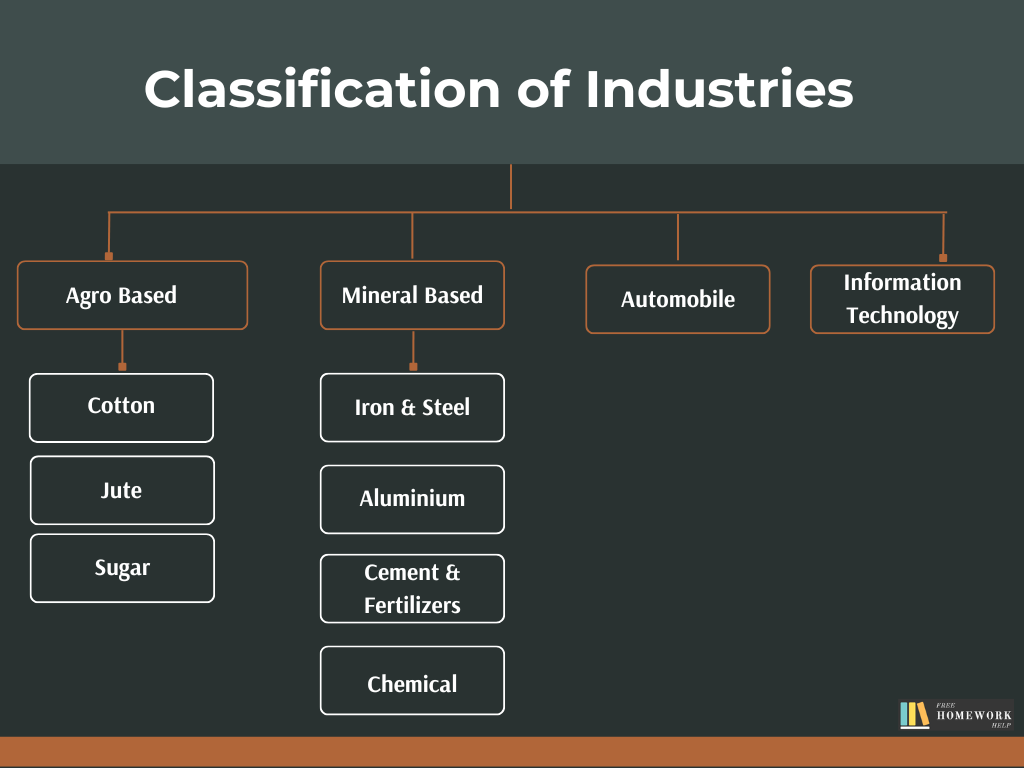
Agro-based Industries
The industries which are dependent on agricultural products for their raw material are called agro-based industries, such as Cotton, jute, silk, woollen textiles, sugar, edible oil, etc. Let’s learn them one by one.
Textile Industry
- It is the only industry in India which is self-sufficient and comprehensive across the value chain, i.e. from raw materials to high-value-added products.
- It contributes to industrial output, employment generation and foreign exchange earnings.
- It contributes 4 per cent to GDP.
Cotton Textiles
- The cotton textile industry is deeply connected to agriculture and provides employment to farmers, cotton pickers, and workers involved in processes like ginning, spinning, weaving, dyeing, designing, packaging, and tailoring. It also supports many related industries such as chemicals, dyes, packaging, and machinery.
- India has a rich history of producing cotton textiles through hand spinning and handloom weaving since ancient times. The first textile mill in India was set up in Mumbai in 1854.
- This industry mainly developed in Maharashtra and Gujarat, as these regions offer several advantages—availability of raw cotton, large markets, good transport network, port access, skilled labour, and a humid climate which is ideal for spinning and weaving.
- India exports cotton textile products to countries like the USA, UK, Russia, France, Eastern Europe, Nepal, Singapore, Sri Lanka, and various African nations.
Jute Textiles
- India is the leading producer of raw jute and jute products in the world.
The first jute mill in India was established in 1859 at Rishra, near Kolkata. - Most of the jute mills are located in West Bengal, along the banks of the Hugli River, because of the following favourable conditions:
- Strong infrastructure, including banking, insurance, and port facilities to support trade and export of jute goods
- Proximity to jute-growing regions for easy access to raw material
- A well-developed network of railways, roadways, and waterways for smooth transportation
- A plentiful water supply is essential for processing jute
- Availability of cheap and skilled labour from states like West Bengal, Bihar, Odisha, and Uttar Pradesh
Sugar Industry
- India is the second-largest sugar producer in the world.
- These were mainly located in Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Punjab, Haryana, and Madhya Pradesh. There were more than 660 sugar mills in India in 2010-11.
- 60% of the mills were located in Uttar Pradesh and Bihar.
- Now, many sugar mills are moving to Maharashtra and other southern/western states because:
- Sugarcane has more sugar (sucrose).
- Due to the cold climate, the crushing season becomes longer.
Cooperative sugar mills work better in these areas.

Mineral-based Industries
The industries which are dependent on mineral products for their raw material are called mineral-based industries, such as Iron and Steel, aluminium, cement, etc. Let’s learn them one by one:
Iron and Steel Industry
- It may be heavy, medium or light depending upon the machinery used.
- These include a lack of proper infrastructure, low labour productivity, low availability of coal and its high cost, irregularity in power supply, etc.
- It is the basic industry as it provides all types of machinery to run all other industries. Steel is required for the manufacture of various engineering goods, construction materials, defence, medical, telephone and scientific equipment and various consumer goods.
- The production and consumption of steel are often considered as an index of the development of a country. India ranks fourth among the world’s crude steel producers and is the largest producer of sponge iron.
- China is also the largest producer of steel and the world’s largest steel consumer.
Aluminium Smelting
- Aluminium smelting is another important industry in India.
- Aluminium is used in everything from cables to aircraft. Bauxite is the raw material used in smelting.
- It has gained popularity in many industries as an alternative to steel, copper, zinc and lead. It is lightweight, corrosion resistant, a good conductor of heat, malleable and becomes stronger when alloyed with other metals.
- It is located in Odisha, West Bengal, Kerala, Uttar Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu.
Chemical Industry
- The chemical industry in India is growing fast.
- It adds about 3% to the country’s GDP.
- It is the 3rd largest in Asia and 12th in the world.
- The industry has both big and small factories. It makes two types of chemicals: organic and inorganic. Organic chemicals include petrochemicals used in making rubber, synthetic fibres, medicines, colours, and plastics.
- Inorganic chemicals include acids and salts like sulphuric acid, nitric acid, caustic soda, soda ash, and alkalis.
Fertiliser Industry
- India is the third-largest producer of nitrogen-based fertilisers.
- It is highest in the Indian states of Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Gujarat, Punjab, Uttar Pradesh, etc.
- The main items produced in this sector of the manufacturing industry are: Nitrogen fertilisers.
- Complex fertilisers contain a combination of phosphate (P), nitrogen (N) and potash (K).
- Phosphatic fertilisers and ammonium phosphate (DAP).
Cement Industry
Cement is used to build houses, roads, bridges, dams, airports, and factories. It is made from raw materials like limestone, silica, and gypsum. The first cement plant was started in Chennai in 1904, and many plants are now set up in Gujarat.
Automobile Industry
The automobile industry makes vehicles like cars, buses, trucks, motorcycles, scooters, and three-wheelers. Most factories are in cities like Gurgaon, Lucknow, Delhi, Kolkata, Chennai, Mumbai, and Pune. This industry helps people travel easily and quickly.
Information Technology and Electronic Industry
- The electronics industry makes things like transistor radios, TVs, telephones, mobile phones, pagers, telephone systems, radars, computers, and other telecom devices.
- Bangalore is known as the Electronic Capital of India.
- Major IT hubs are in Bangalore, Noida, Mumbai, Chennai, Hyderabad, and Pune.
- This industry gives jobs to a large number of people.
- It also earns a lot of foreign money for India, especially because of the fast-growing BPO (Business Process Outsourcing) sector.
Industrial Pollution And Environmental Degradation
Industries cause four main types of pollution:
Air Pollution – Caused by smoke and harmful gases like CO₂ and SO₂ from factories, refineries, and smelters. It harms humans, animals, and plants.
Water Pollution – This happens when industries like textiles, chemicals, and tanneries dump waste into rivers.
Thermal Pollution – Caused when hot water from thermal plants is released into rivers.
Noise Pollution – Created by loud machines, which can damage hearing.
Control of Environmental Degradation
Ways to reduce water pollution from industries:
- Use less water by recycling it in different steps.
- Collect rainwater to use in factories.
- Clean hot water and waste before putting it into rivers or ponds.
Ways to reduce air pollution:
- Fit factory chimneys with filters like scrubbers and electrostatic devices.
- Use cleaner fuels like oil or gas instead of coal.
Ways to reduce noise pollution:
- Use quieter machines and add silencers to generators.
- Use sound-absorbing materials and wear earplugs when needed.
Read More: NCERT Solution For Class 10 Geography Chapter 5
FAQ
Why is manufacturing important for the economy?
It helps in industrial growth and provides jobs.
What is an agro-based industry?
An industry that uses agricultural products as raw material.
Name two major polluting industries.
Thermal power plants and chemical industries.
Conclusion
You can find all CBSE Class 10 Social Science notes—covering History, Political Science, Geography, and Economics—in one convenient place. Keep learning and stay connected for the latest updates on CBSE and NCERT. Don’t forget to subscribe to our YouTube channel for interactive Social Science video lessons!
