In this post, we have provided the Resources and Development Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 Notes to introduce you to resources and their classification. In this chapter, you will learn about the development of resources and resource planning in India as well as land resources and the different types of soils found in India. Finally, the chapter provides concepts of Soil Erosion and Soil Conservation.
Resources and Development Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 Notes
The things which are available in our environment & can be used to satisfy our needs are called resources. The resources can be classified in the following ways:
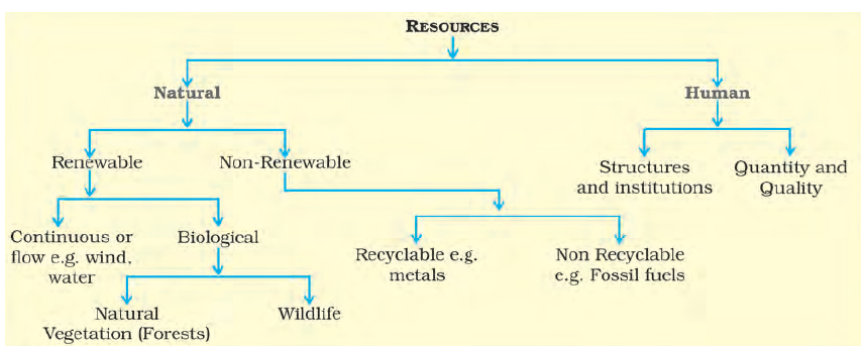
Types of Resources Class 10 Geography Chapter 1
Based on Origin
Biotic Resources: All living things which are obtained from the biosphere are called biotic resources.
Examples- are human beings, flora, and fauna, livestock, etc.
Abiotic Resources: All non-living things are called abiotic resources.
Examples-rocks and metals.
Based on Exhaustibility
Renewable Resources: The resources that can be renewed by using the process of physical, and chemical are called renewable resources.
Examples- are solar & wind energy, water, forests, and wildlife, etc.
Non-Renewable Resources: The resources whose stock gets reduced and exhausted with use are known as non-renewable resources. These can not be recycled.
Examples- are fossil fuels like coal, petroleum, and minerals.
Based on Ownership
Individual Resources: These resources are owned by individuals e.g. plots, houses, cars, wells, etc.
Community-Owned Resources: The resources which are available to all the members of the community are called community-owned resources e.g. public parks, picnic spots, playgrounds, etc.
National Resources: The resources that belonged to the nation are called national resources e.g. flora & fauna, land division, and political territories.
International Resources: These resources are operated by international institutions. The oceanic resources that no individual country can utilize without the coincidence of international institutions.
Based on the Status of Development
Potential Resources: The resources which are found in a region, but not have been yet utilized. are called potential resources.
Examples- The western parts of India ( Rajasthan & Gujarat) have a large potential development in wind and solar energy but have not been developed properly for a long time.
Developed Resources: The resources which are developed and whose quantity & quality have been determined for utilization.
Stock: The resources which can satisfy human needs but human beings do not have the appropriate technology to use are called stocks. Examples- Hydrogen can be used as a rich source of energy but we do not have the knowledge to use it.
Reserves: These can be used to meet future requirements.
Example- The water in the dams, forests, etc. is a reserve that can be used in the future.
What is Development of Resources Class 10?
Resources are gifts of nature but these have been used by human beings aimlessly and the following major problems have been created due to this.
- Indiscriminate use of resources to satisfy the greed of a few individuals.
- Accumulation of resources in a few hands divides society into ‘haves’ and nave-nots’.
- It has led to global warming, ozone layer depletion, environmental pollution, and land degradation.
Resource planning is needed for the sustainable existence of all forms of life.
Sustainable Development of Resources
Sustainable Economic Development is a development that should take place without damaging the environment, and should not compromise with the needs of future generations.”
The first international Earth Summit was held in Rio de Janeiro in 1992, attended by a hundred countries.
Adopted Agenda 21 to achieve global sustainable development and to combat poverty, and disease in the world.
What is Resource Planning?
In India, there are a few regions that are independent in terms of the availability of resources and there are a few regions that lack some vital resources.
For example, Arunachal Pradesh has water access but needs to improve infrastructural development.
Rajasthan has an abundance of solar and wind energy but lacks water resources.
Resource Planning in India
In India, there is a need to plan for resources but resource planning is a complex process that involves:
i) To distinguish proof and stock of assets and resources across the regions of the country like surveying, mapping, and qualitative and quantitative estimation and measurement of the resources.
ii) To know about technology, skill, and institutional setup for implementing resource development plans.
iii) To match the resource development plans with all national development plans.
Indian resource development depends on technology, the quality of human resources, and the historical experiences of people. India has made efforts to achieve the goals of resource planning from the First Five Year Plan launched after Independence.
Conservation of Resources Class 10
It is very important to the conservation of natural resources because these resources are being reduced very rapidly. The reduction of natural resources has ill effects on the environment which in turn harms human life.
Land Resources | Class 10 Geography Chapter 1
The land is an important natural resource. It supports natural vegetation, wildlife, and human life. All economic activities are performed on land. Land provides suitable places for transport and communication systems. It is an asset of a magnitude.
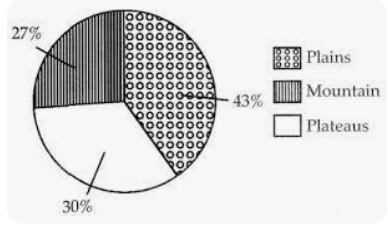
Relief Features of India: India has a variety of physical features, namely; mountains, plateaus, plains, and islands as shown below:
Plains – covering 43% area
mountains – covering 30% area
Plateaus – covering 27% area
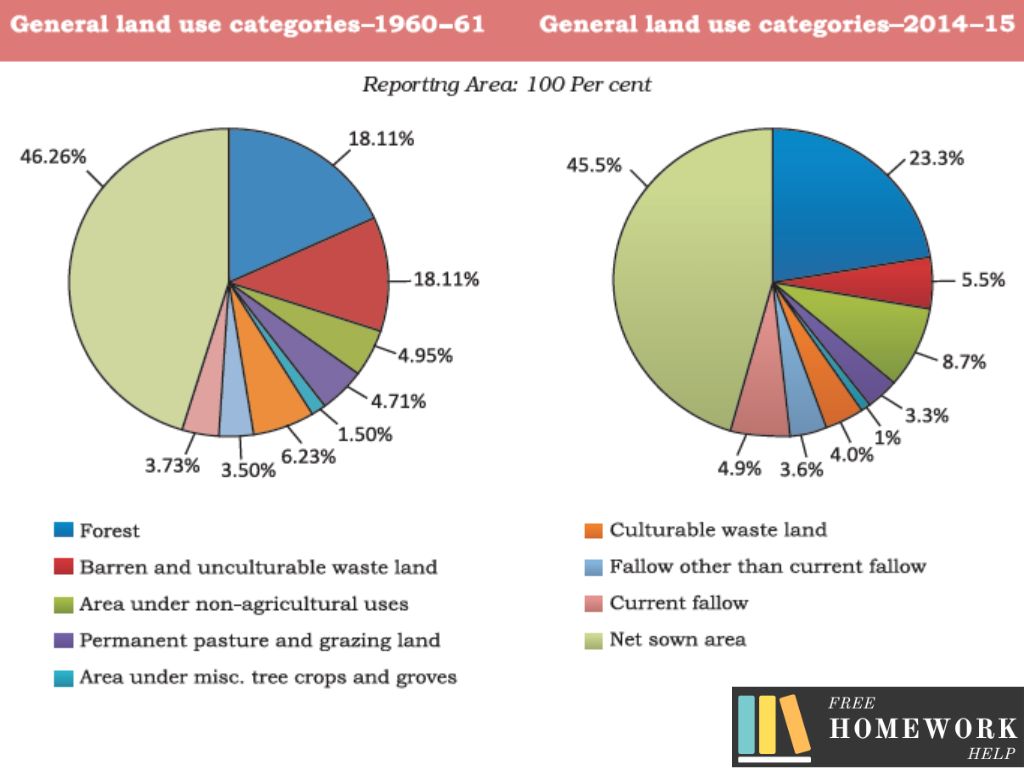
Land Utilisation: Land is used for the following purposes:
1. Forest
2. Barren and wasteland are not available for cultivation.
3. Land is used to build buildings, roads, factories, etc.
4. Land is used for permanent pastures and grazing land.
5. Fallow land that is left without cultivation for one or less than one agricultural year.
6. Net Sown area that is sown more than once a year. It is known as the gross cropped area.
Land Use Pattern in India
The use of land in India is determined by the following two factors-
i) Physical factors- topography, climate, soil types
ii) Human Factors- population density, technological capability, culture, traditions, etc.
The data on land use patterns are given below.
Land Degradation and Conservation Measures Class 10
Land Degradation is the process in which the quality of land is destroyed due to the continuous use of land over a long period without taking measures and managing it. There are the following reasons for land degradation:
1. deforestation
2. overgrazing
3. mining
4. over-irrigation
5. land and water pollution
The following measures can be taken to solve the problem of land degradation.
1. Afforestation and proper management of grazing
2. Planting of shelter belts for plants.
3. Control overgrazing.
4. By growing thorny bushes in arid regions.
5. Proper management of wastelands.
6. Control of mining activities
7. Proper discharge and disposal of industrial wastes.
Soil AS A Resource | Class 10 Geography Chapter 1
Soil is the most important renewable resource in nature. It helps plants to grow and supports different types of living organisms on the earth.
i) Soil is a living system.
ii) It takes millions of years to form up to a few cm in depth.
iii) The important factors which affect the formation of soil are relief, parent rock, climate, vegetation, and time.
iv) Various forces of nature such as the action of running water, changes in temperature, wind, glaciers, etc. contribute to the formation of soil.
Classification of Soils Class 10
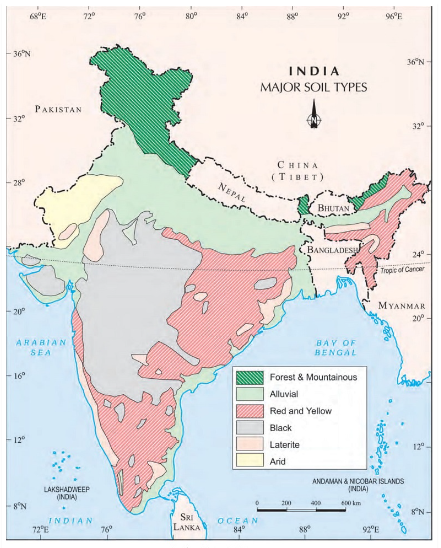
The soils of India are classified into different types based on soil formation, colour, thickness, texture, age, etc.
1. Alluvial Soil:
- The entire northern plains are made up of alluvial soil.
- These have been deposited by three important Himalayan river systems- Indus, Brahmaputra, and Ganga.
- It is also found in the eastern coastal plains, particularly in the deltas of the Mahanadi, the Godavari, the Krishna, and the Kaveri rivers.
- It consists of various proportions of sand, silt, and clay.
- Based on age. it can be classified into two types:
Old (Bangar): The Bangar soil has a higher concentration of Kanker nodules. It is less fertile than the Khadar.
New (Khadar): It has less concentration of Kanker nodules than Bangar. It is more fertile than the Bangar. - Alluvial soil is very fertile. It contains an adequate proportion of potash, phosphoric acid, and lime.
- It is ideal for the growth of sugarcane, paddy, wheat, and other cereal and pulse crops.

2. Black Soil:
- Black soil is found in the northwest of the Deccan Plateau and is made up of lava flows.
- It covers the plateaus of Maharashtra, Saurashtra, Malwa, Madhya Pradesh, and Chhattisgarh.
- It is made up of clayey material and is well-known for its capacity to hold moisture.
- It is nutrient-rich and contains calcium carbonate, magnesium, potash, and lime.
- It is black in colour and is also known as regur soil.
- It is ideal for growing cotton.
- It is sticky when wet and difficult to work on unless tilled immediately after the first shower or during the pre-monsoon period.

3. Red and Yellow Soil:
- Red soil develops on crystalline igneous rocks in areas of low rainfall in the eastern and southern parts of the Deccan plateau.
- It is reddish in colour due to the diffusion of iron in crystalline and metamorphic rocks.
- It looks yellow when it happens in a hydrated structure.
- It is found in Odisha, Chhattisgarh, southern parts of the middle Ganga plain, and along the Piedmont zone of the Western Ghats.

4. Laterite Soil:
- It is found in Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Madhya Pradesh, and the hilly areas of Odisha and Assam.
- It develops in areas with high temperatures and heavy rainfall.
- It is reasonable for the development of manures and fertilizers.
- It is extremely valuable for growing tea and coffee.

5. Arid Soil:
- It is found in western Rajasthan where it becomes cultivable after proper irrigation.
- It is generally sandy in texture and saline in nature.
- It ranges from red to brown in colour.
- In some areas, the salt content is very high from where common salt is obtained by evaporating the water.

6. Forest Soil:
- It is found in hilly and mountain areas.
- Its texture varies according to the mountain environment where they are formed.
- It is loamy and silty on the valley sides and coarse-grained on the upper slopes.
- It is fertile on the river terraces and alluvial fans.
- It experiences denudation and is acidic with low humus content in the snow-covered areas of the Himalayas.
What is Soil Erosion?
Soil erosion is a slow process that occurs when the effect of water or wind d removes soil particles, causing the soil to deteriorate. This is caused due to human activities like deforestation, overgrazing, construction, mining, etc. & natural forces like wind, glaciers, and water lead to soil erosion.
The running water cuts through the clayey soils and forms gullies and is also caused due to defective methods of farming-ploughing in a wrong manner.
What is Soil Conservation?
There are so many ways to conserve the soil.
i) Contour Ploughing:
In hilly areas, contour ploughing should be practised to check the flow of water down the slopes.
ii) Terrace Farming:
steps can be cut out on the slopes making terraces to restrict soil erosion.
iii) Strip Cropping:
Large fields can be divided into strips to break up the force of the wind.
iv) Planting of Shelter Belt:
Planting a line of trees to create shelter checks soil erosion. Rows of such trees are called shelter belts.
The below map shows the different types of soils found in India:
Also Read: Power Sharing Class 10 Notes | Easy Ncert Solutions
FAQs | Class 10 Geography Chapter 1
What is resource and development class 10th?
Resource development means the development that takes place without damaging the environment. The development in the present should not destroy the ability of future generations to meet their needs.
What are the different types of natural resources and how are they classified?
Natural resources can be classified into two main types: renewable and non-renewable. Renewable resources such as sunlight, wind, water, and forests. Non-renewable resources such as fossil fuels and minerals.
What is the importance of resources in development class 10?
Resources are used as raw materials to satisfy the needs and comforts of human beings. Natural resources are a source of agricultural activities which adds to the economic importance.
What are resources in short notes?
Resource refers to all the materials available in our environment which are technically accessible, economically viable, and culturally sustainable and help us to satisfy our needs and wants.
What is resource planning class 10th?
Resource planning is a process that involves identification, survey, mapping, qualitative and quantitative estimation of resources, etc. in different regions of the country.
What are resources?
The resource is a physical material that is needed by human beings such as land, air, and water.
What are natural resources called?
Natural resources are materials obtained from the earth that are used to support life and meet people’s needs as Oil, coal, natural gas, metals, stones, and sand are natural resources.
What is the importance of resources?
Resources meet the needs and facilities of human beings. These are a source of agricultural activities that add economic importance. They also provide employment opportunities.
What is a man-made resource?
Man-made resources are created by humans using raw materials obtained from natural resources. Examples- plastics, rubber, paper, brass, and various other materials.
Is water a natural resource?
Yes, Water is a natural resource that supports ecosystems, industry, agriculture, households, and recreation.
Conclusion
I hope the information given above regarding Resources and Development Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 Notes has been helpful to you. If you have any other queries about NCERT Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 Resources and Development, feel free to reach us so that we can get to you at the earliest possible.
